doktorekg.com
Ectopic Atrial Tachycardia
Diagnostic criteria
 Heart rate is > 100/minute.
Heart rate is > 100/minute.
 Every P wave may or may not be followed by a QRS complex.
Every P wave may or may not be followed by a QRS complex.
 If every P wave is followed by a QRS complex: ectopic atrial tachycardia.
If every P wave is followed by a QRS complex: ectopic atrial tachycardia.
 If some P waves are followed by QRS complexes: ectopic atrial tachycardia with block.
If some P waves are followed by QRS complexes: ectopic atrial tachycardia with block.
 Since the impulse originates from an ectopic atrial focus
the P waves have a different configuration from that of the sinus wave.
Since the impulse originates from an ectopic atrial focus
the P waves have a different configuration from that of the sinus wave.
 The recognization of differently shaped P waves in ectopic atrial tachycardia may require the inspection of previous ECGs for comparison.
The recognization of differently shaped P waves in ectopic atrial tachycardia may require the inspection of previous ECGs for comparison.
 When left untreated, incessant atrial tachycardias may give rise to heart failure.
When left untreated, incessant atrial tachycardias may give rise to heart failure.

ECG 1. Ectopic atrial tachycardia in a patient with systemic arterial hypertension. P waves are negative in leads D2 and D3.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 2a. Above ECG is from a 64 years-old man with coronary artery disease, hypertension and aneurysm of the ascending aorta.
Runs of ectopic atrial tachycardia and some sinus beats are seen.
P wave rate is about 115/minute.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 2b. The above ECG belongs to the same patient.
Atrial premature beats are seen.
An atrial premature beat initiates an episode of ectopic atrial tachycardia.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 3. The ECG above belongs to a 69 years-old man with coronary artery disease.
He had undergone coronary artery bypass graft surgery and tricuspid annuloplasty in the past.
The rhythm may seem like atrial fibrillation at first glance, but it is not.
The RR intervals are usually regular. P waves become visible when the level of AV block increases.
Isoelectric flat line between the P waves show that the rhythm is not atrial flutter.
If looked carefully, P waves deforming the descending limb of the preceding T waves may be seen in inferior leads.
The rhythm is ectopic atrial tachycardia (with block; 2:1 most of the time).
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 4a. The ECG above belongs to a 85 years-old woman with coronary artery disease.
She complains of palpitation. Right bundle branch block is seen.
The heart rate is 121/minute. What is the rhythm?
Is it sinus tachycardia? Can you see the P waves?
Do you think that the PR interval is normal? Is it sinus tachycardia?
At a ventricular rate of 121/minute, it is easy to misdiagnose this rhyhtm as sinus tachycardia, at first glance.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 4b. The ECG above belongs to the same woman.
It was recorded 30 seconds after the ECG 4a.
What is the rhythm?
Do you see the P waves? Do you think that the PR interval is normal?
Do you think that there is sawtooth appearance?
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 4c. The above rhythm tracing belongs to the same woman.
It was recorded at a calibration of 20 mm/mV to better see the details.
P waves are clearly seen. Atrial rate (P wave rate) is 240/minute.
Not all P waves are conducted to ventricles. This is ectopic atrial tachycardia with block.
This is not atrial flutter, there is no sawtooth appearance: a flat baseline between the P waves is seen.
Since frequent temporary increases in AV block level revealed ectopic P waves, we did not need to use Adenosine
in this patient.
Click here for a more detailed ECG
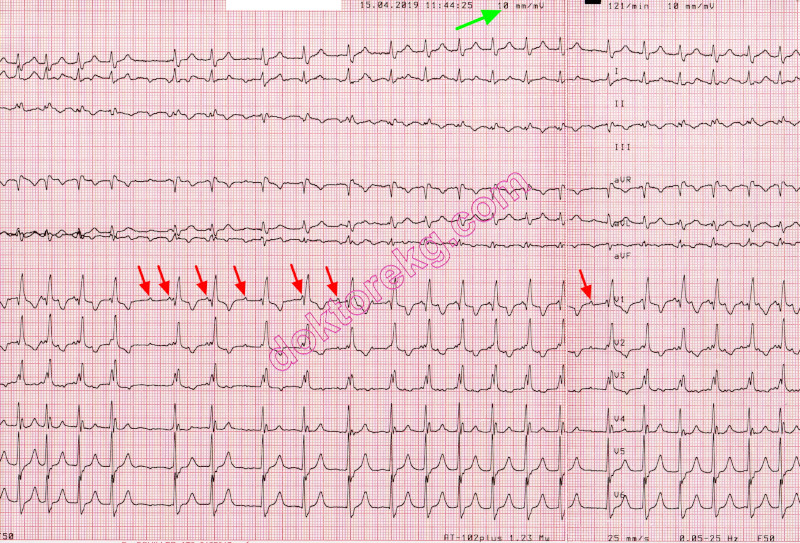
ECG 4d. The above rhythm tracing belongs to the same woman.
It was recorded at a calibration of 10 mm/mV
P waves are seen. Not all P waves are conducted to the ventricles.
This is ectopic atrial tachycardia with block.
Since frequent temporary increases in AV block level revealed ectopic P waves, we did not need to use Adenosine
in this patient.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5a. The ECG above belongs to a 12 years-old boy with palpitation.
His ECHOcardiography is normal: no structural heart disease.
The rhythm is ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration.
This ECG was recorded on 22nd February.2019
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5b. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 23rd August.2019.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration is seen.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5c. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 23rd August.2019.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia is seen.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5d. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 5th September.2019.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration is seen.
This ECG was recorded just before his electrophysiological study and successful ablation.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5e. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 5th September.2019.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration is seen.
This ECG was recorded just before his electrophysiological study and successful ablation.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5f. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 5th September.2019.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration is seen.
This ECG was recorded just before his electrophysiological study and successful ablation.
When left untreated, these incessant tachycardias may give rise to left ventricular failure and dilation.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5g. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 6th September.2019.
Normal sinus rhythm is seen. Ectopic atrial tachycardia is abolished.
This ECG was recorded one day after his electrophysiological study and successful ablation.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 6a. The ECG above belongs to a 7 years-old girl with the complaint of palpitation.
Her ECHOcardiography was normal: no structural heart disease.
Short-lasting episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration are seen.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 6b. The ECG above belongs to the same patient.
Short-lasting episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration are seen.
P wave morphology is not the same.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) showed atrial tachycardia originating from multiple foci.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 6c. The ECG above belongs to the same patient.
Short-lasting episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia is seen.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) showed atrial tachycardia originating from multiple foci.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 6d. The ECG above belongs to the same patient.
Short-lasting episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia is seen.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) showed atrial tachycardia originating from multiple foci.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 6e. The above 3-channel rhythm Holter tracing belongs to the same patient.
Atrial fibrillation is seen.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) showed atrial tachycardia originating from multiple foci, and
manipulation of the catheter frequently induced atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 7a. The ECG above belongs to a 75 years-old man with prosthetic aortic valve.
This ECG was recorded before the onset of Amiodarone infusion.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 7b. The ECG above belongs to the same patient.
It was recorded after Amiodarone infusion.
It has a standard calibration (10 mm/mV) and paper speed (25 mm/second).
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 7c. The ECG above belongs to the same patient.
It was recorded 2 minutes after the ECG 7b.
Now, the calibration is increased: 20 mm/mV.
This adjustment of calibration showed P waves clearly.
The rhythm is focal atrial tachycardia with increased AV block due to Amiodarone infusion.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 8a. The ECG above belongs to a 71 years-old man.
What is the rhythm?
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 8b. The ECG above belongs to the same man.
P waves are seen. The rhythm is atrial tachycardia.
This man is not under Digoxin therapy.
The ECG was recorded at standard paper speed (25 mm/sec.) and calibration (10 mm/mV).
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 8c. The ECG above belongs to the same man.
P waves are seen clearly. The rhythm is atrial tachycardia.
This ECG was recorded at standard paper speed (25 mm/sec.) but high calibration (20 mm/mV).
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 8d. The above rhythm tracing belongs to the same man.
It was recorded at a paper speed of 50 mm/sec. and 20 mm/mV calibration.
P waves are seen.
Some P waves coincide with the QRS complexes.

ECG 9. The 3-channel ECG tracing above is from a 24-hour ECG (rhythm Holter) recording. The third P wave from the left side has a different morphology (an atrial premature contraction-APC). The second APC starts a short-lasting atrial tachycardia episode. The last two beats are sinus beats.
Click here for a more detailed ECG
 Heart rate is > 100/minute.
Heart rate is > 100/minute.
 Every P wave may or may not be followed by a QRS complex.
Every P wave may or may not be followed by a QRS complex.
 If every P wave is followed by a QRS complex: ectopic atrial tachycardia.
If every P wave is followed by a QRS complex: ectopic atrial tachycardia.
 If some P waves are followed by QRS complexes: ectopic atrial tachycardia with block.
If some P waves are followed by QRS complexes: ectopic atrial tachycardia with block.
 Since the impulse originates from an ectopic atrial focus
the P waves have a different configuration from that of the sinus wave.
Since the impulse originates from an ectopic atrial focus
the P waves have a different configuration from that of the sinus wave.
 The recognization of differently shaped P waves in ectopic atrial tachycardia may require the inspection of previous ECGs for comparison.
The recognization of differently shaped P waves in ectopic atrial tachycardia may require the inspection of previous ECGs for comparison.
 When left untreated, incessant atrial tachycardias may give rise to heart failure.
When left untreated, incessant atrial tachycardias may give rise to heart failure.

ECG 1. Ectopic atrial tachycardia in a patient with systemic arterial hypertension. P waves are negative in leads D2 and D3.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 2a. Above ECG is from a 64 years-old man with coronary artery disease, hypertension and aneurysm of the ascending aorta.
Runs of ectopic atrial tachycardia and some sinus beats are seen.
P wave rate is about 115/minute.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 2b. The above ECG belongs to the same patient.
Atrial premature beats are seen.
An atrial premature beat initiates an episode of ectopic atrial tachycardia.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 3. The ECG above belongs to a 69 years-old man with coronary artery disease.
He had undergone coronary artery bypass graft surgery and tricuspid annuloplasty in the past.
The rhythm may seem like atrial fibrillation at first glance, but it is not.
The RR intervals are usually regular. P waves become visible when the level of AV block increases.
Isoelectric flat line between the P waves show that the rhythm is not atrial flutter.
If looked carefully, P waves deforming the descending limb of the preceding T waves may be seen in inferior leads.
The rhythm is ectopic atrial tachycardia (with block; 2:1 most of the time).
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 4a. The ECG above belongs to a 85 years-old woman with coronary artery disease.
She complains of palpitation. Right bundle branch block is seen.
The heart rate is 121/minute. What is the rhythm?
Is it sinus tachycardia? Can you see the P waves?
Do you think that the PR interval is normal? Is it sinus tachycardia?
At a ventricular rate of 121/minute, it is easy to misdiagnose this rhyhtm as sinus tachycardia, at first glance.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 4b. The ECG above belongs to the same woman.
It was recorded 30 seconds after the ECG 4a.
What is the rhythm?
Do you see the P waves? Do you think that the PR interval is normal?
Do you think that there is sawtooth appearance?
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 4c. The above rhythm tracing belongs to the same woman.
It was recorded at a calibration of 20 mm/mV to better see the details.
P waves are clearly seen. Atrial rate (P wave rate) is 240/minute.
Not all P waves are conducted to ventricles. This is ectopic atrial tachycardia with block.
This is not atrial flutter, there is no sawtooth appearance: a flat baseline between the P waves is seen.
Since frequent temporary increases in AV block level revealed ectopic P waves, we did not need to use Adenosine
in this patient.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 4d. The above rhythm tracing belongs to the same woman.
It was recorded at a calibration of 10 mm/mV
P waves are seen. Not all P waves are conducted to the ventricles.
This is ectopic atrial tachycardia with block.
Since frequent temporary increases in AV block level revealed ectopic P waves, we did not need to use Adenosine
in this patient.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5a. The ECG above belongs to a 12 years-old boy with palpitation.
His ECHOcardiography is normal: no structural heart disease.
The rhythm is ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration.
This ECG was recorded on 22nd February.2019
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5b. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 23rd August.2019.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration is seen.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5c. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 23rd August.2019.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia is seen.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5d. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 5th September.2019.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration is seen.
This ECG was recorded just before his electrophysiological study and successful ablation.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5e. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 5th September.2019.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration is seen.
This ECG was recorded just before his electrophysiological study and successful ablation.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5f. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 5th September.2019.
Ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration is seen.
This ECG was recorded just before his electrophysiological study and successful ablation.
When left untreated, these incessant tachycardias may give rise to left ventricular failure and dilation.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 5g. The ECG above belongs to the same boy.
It was recorded on 6th September.2019.
Normal sinus rhythm is seen. Ectopic atrial tachycardia is abolished.
This ECG was recorded one day after his electrophysiological study and successful ablation.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 6a. The ECG above belongs to a 7 years-old girl with the complaint of palpitation.
Her ECHOcardiography was normal: no structural heart disease.
Short-lasting episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration are seen.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 6b. The ECG above belongs to the same patient.
Short-lasting episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia with intermittent aberration are seen.
P wave morphology is not the same.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) showed atrial tachycardia originating from multiple foci.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 6c. The ECG above belongs to the same patient.
Short-lasting episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia is seen.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) showed atrial tachycardia originating from multiple foci.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 6d. The ECG above belongs to the same patient.
Short-lasting episodes of ectopic atrial tachycardia is seen.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) showed atrial tachycardia originating from multiple foci.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 6e. The above 3-channel rhythm Holter tracing belongs to the same patient.
Atrial fibrillation is seen.
Electrophysiological study (EPS) showed atrial tachycardia originating from multiple foci, and
manipulation of the catheter frequently induced atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter.
Pediatric Cardiologist Prof. Dr. Tevfik Karagoz has donated the above ECG to our website.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 7a. The ECG above belongs to a 75 years-old man with prosthetic aortic valve.
This ECG was recorded before the onset of Amiodarone infusion.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 7b. The ECG above belongs to the same patient.
It was recorded after Amiodarone infusion.
It has a standard calibration (10 mm/mV) and paper speed (25 mm/second).
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 7c. The ECG above belongs to the same patient.
It was recorded 2 minutes after the ECG 7b.
Now, the calibration is increased: 20 mm/mV.
This adjustment of calibration showed P waves clearly.
The rhythm is focal atrial tachycardia with increased AV block due to Amiodarone infusion.
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 8a. The ECG above belongs to a 71 years-old man.
What is the rhythm?
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 8b. The ECG above belongs to the same man.
P waves are seen. The rhythm is atrial tachycardia.
This man is not under Digoxin therapy.
The ECG was recorded at standard paper speed (25 mm/sec.) and calibration (10 mm/mV).
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 8c. The ECG above belongs to the same man.
P waves are seen clearly. The rhythm is atrial tachycardia.
This ECG was recorded at standard paper speed (25 mm/sec.) but high calibration (20 mm/mV).
Click here for a more detailed ECG

ECG 8d. The above rhythm tracing belongs to the same man.
It was recorded at a paper speed of 50 mm/sec. and 20 mm/mV calibration.
P waves are seen.
Some P waves coincide with the QRS complexes.

ECG 9. The 3-channel ECG tracing above is from a 24-hour ECG (rhythm Holter) recording. The third P wave from the left side has a different morphology (an atrial premature contraction-APC). The second APC starts a short-lasting atrial tachycardia episode. The last two beats are sinus beats.
Click here for a more detailed ECG